Search Results for: physiological processes
Physiological processes
physiological processes The functions of living organisms and their parts, and the physical and chemical factors and... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Chronobiology
Chronobiology Definition Chronobiology is a branch of biology that studies time-related phenomena (e.g., biological... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Animal Water Regulation
Homeostatic control, a set environment, and how evolution and natural selection drives a species to adapt to its environment... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Prostaglandin
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins A group of eicosanoids, structurally characterized as 20-carbon unsaturated fatty... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
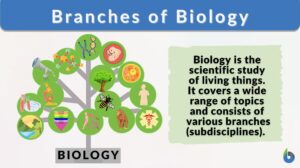
Branches of biology
What is a Branch of Biology? A branch of biology is a specialized field or a sub-discipline in a much broader field of... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. WrightDepartment of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Milieu interieur
Definition noun (1) Literally means: the environment within. (2) The outside of the cells inside the body of an organism,... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
photobiology
Photobiology Definition Photobiology, the biology of light, is a subdiscipline in biology. It focuses on the effects of... Read More
Dissolved oxygen
Definition noun The amount of free oxygen dissolved in water, expressed in mg/L, parts per million (ppm), or in percent of... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Neuropsychology
Definition noun The scientific study of the physiological basis of psychological processes Supplement Neuroscience is the... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and BehaviorHaving discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Sexual selection
What is Sexual Selection? The definition of sexual selection is very interesting in biological terms. The sexual selection... Read More







![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)